POSTER ABSTRACTS
Materials should NOT be shared with those that are not registered for the conference. Poster abstracts are not proofed for spelling and/or grammar errors.
The poster and/or other information contained on this website may NOT be downloaded and/or used without prior written permission from all authors on the project. If you would like to be connected with the author(s), please email [email protected].
Central CO2 chemosensitivity and autonomic function in patients with epilepsy
Marie-Anne Melone, MD1, Rup K. Sainju, MD2, Deidre N. Dragon, BSS2, Harold B. Winnike, RRT3, Mark Chapleau, MD1,4, George B. Richerson, PhD2,4,5, Brian K. Gehlbach, MD1,2
1Department of Internal Medicine, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA
2Department of Neurology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA
3Institute of Clinical and Translational Science, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA
4Department of Molecular Physiology and Biophysics, Iowa Neuroscience Institute, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA
5VA Medical Center, Iowa City, IA
Abstract
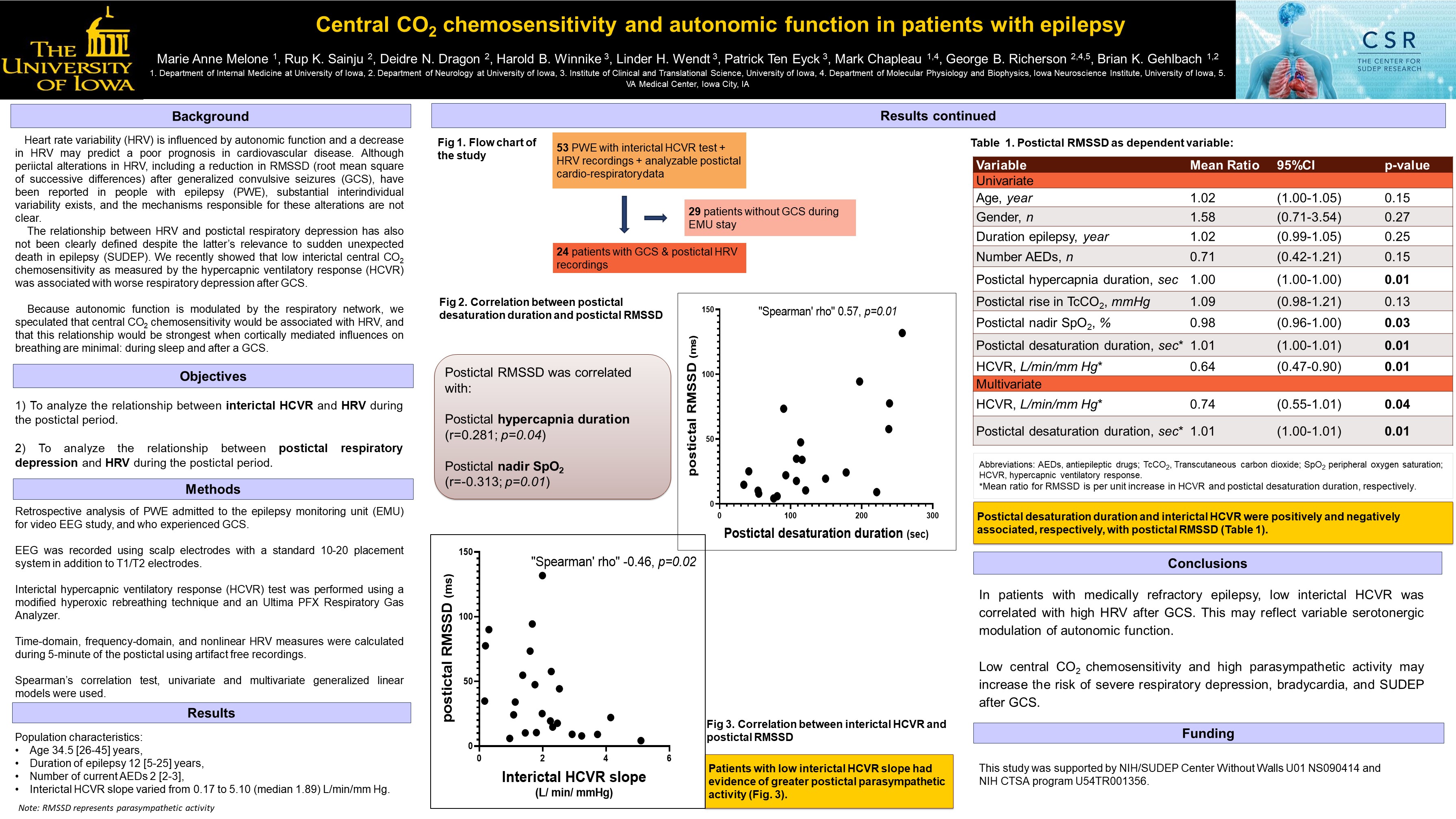
Objective: In people with epilepsy at risk for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP), heart rate variability (HRV) studies have shown substantial interindividual variability that is largely unexplained. We recently showed that patients with low interictal central CO2 chemosensitivity (the hypercapnic ventilatory response, or HCVR) experience worse respiratory depression after a generalized convulsive seizure (GCS). Because autonomic function is modulated by the respiratory network, we speculated that HCVR would also be associated with HRV. We therefore analyzed the relationship between interictal HCVR and HRV during the postictal period.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of patients with medically refractory epilepsy admitted to the epilepsy monitoring unit for video EEG and cardiorespiratory study, and who experienced GCS. The interictal HCVR was measured using a modified hyperoxic rebreathing technique. Time-domain, frequency-domain, and nonlinear HRV measures were calculated during 5-minute of postictal artifact free recordings.
Results: 24 patients had both a GCS and an interictal HCVR for analysis with median age 34.5 [26-45] years, median duration of epilepsy 12 [5-25] years, and median number of current antiepileptic drugs 2 [2-3]. Interictal HCVR slope was inversely correlated with postictal RMSSD (rho -0.46, P=0.02) and SD1 (rho -0.46, P=0.02). In multivariate analyses, we found postictal desaturation duration and interictal HCVR were positively and negatively associated, respectively, with postictal RMSSD (mean estimate 1.01, 95%CI 1 to 1.01, P=0.01; mean estimate 0.74, 95%CI 0.55 to 1.01, P=0.04 respectively).
Conclusion: In patients with medically refractory epilepsy, low interictal HCVR is associated with high HRV after GCS, suggesting serotonergic modulation of autonomic function.
Access PDF version to expand view.